ED & Disordered Eating
ED & disordered eating
ED & disordered eating: healing from unhealthy patterns
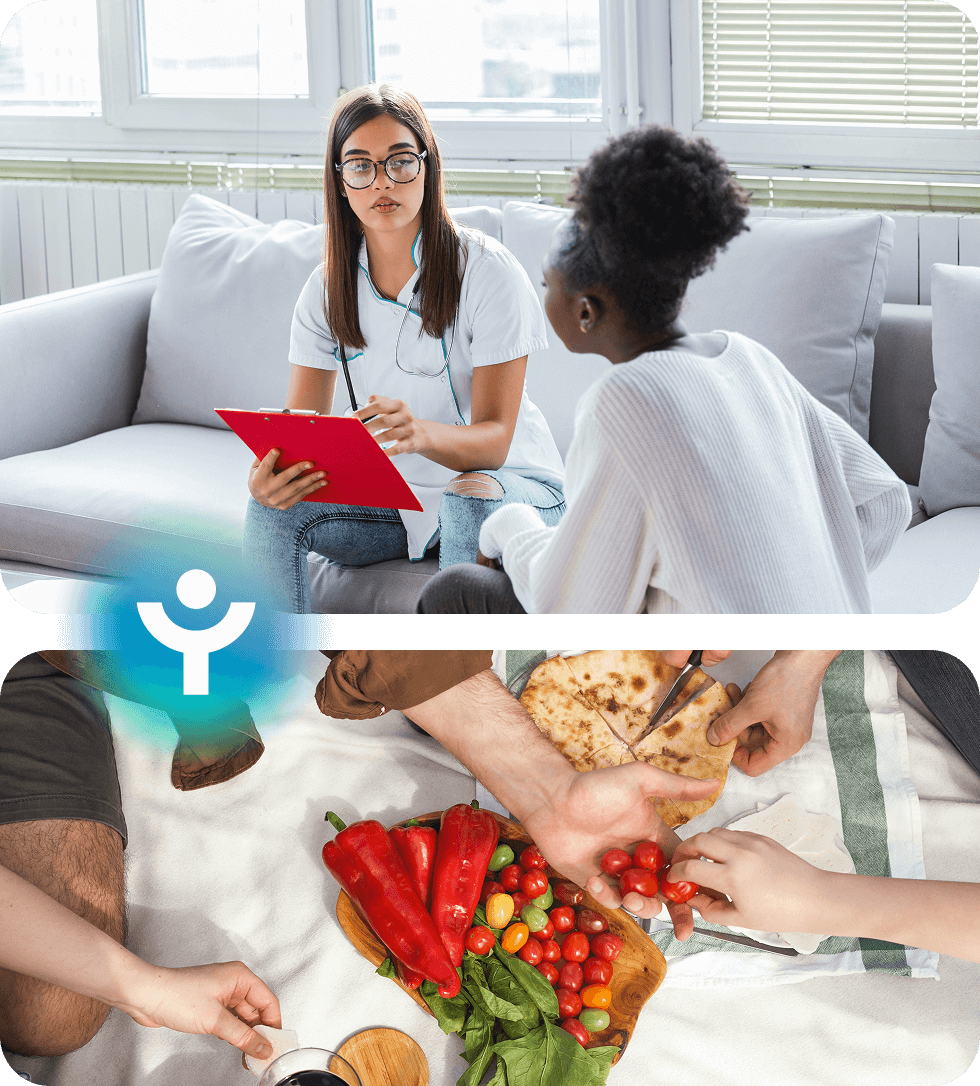
ED (Eating Disorders) and disordered eating refer to a range of unhealthy eating behaviors that can negatively impact both mental and physical health. While traditional eating disorders like anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa, and binge eating disorder are well-known, disordered eating can also include patterns of chronic dieting, emotional eating, or restrictive eating that don’t necessarily meet the clinical criteria for a specific diagnosis but still lead to significant distress.
These behaviors often stem from underlying issues such as low self-esteem, body image concerns, trauma, and emotional distress. Disordered eating can take a toll on mental health, contributing to anxiety, depression, and obsessive thoughts about food, weight, and body image. At Modyfi, we take an integrative approach to treating ED and disordered eating by addressing both the emotional and physiological aspects of the condition. Therapy, nutritional support, mindfulness, and functional medicine are key components in helping individuals rebuild a healthy relationship with food, restore body trust, and promote long-term recovery.

FAQs
ED (eating disorders) and disordered eating encompass a range of unhealthy eating behaviors that can negatively affect both mental and physical health. While eating disorders like anorexia, bulimia, and binge eating disorder are well-defined, disordered eating may include behaviors like chronic dieting, overeating, or emotional eating that don’t necessarily meet the clinical criteria for a specific diagnosis but still lead to significant distress.
ED and disordered eating often result from a combination of psychological, emotional, biological, and societal factors. These may include low self-esteem, a negative body image, trauma, societal pressure to conform to certain standards of beauty or body size, and genetic predisposition. Emotional stress and a desire to control food intake can also contribute to disordered eating behaviors.
Disordered eating often leads to negative emotions such as shame, guilt, anxiety, and depression. The preoccupation with food, body image, and weight can take up a significant portion of a person’s thoughts, causing distress and interfering with daily functioning. The cycle of restricting food, overeating, or using food as a coping mechanism can lead to a lack of emotional regulation and increased mental health challenges.
ED and disordered eating can lead to serious physical health issues, including malnutrition, electrolyte imbalances, gastrointestinal problems, cardiovascular issues, and weakened immunity. Chronic disordered eating can also affect metabolism, hormonal balance, and bone density, making it essential to address these behaviors to prevent long-term health complications.
Diagnosis involves a thorough evaluation by a healthcare provider, which includes assessing eating patterns, behaviors, and any related physical and psychological symptoms. A comprehensive approach includes understanding the emotional and psychological factors driving disordered eating behaviors and ruling out any underlying medical conditions.
Therapy, particularly Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT), is widely used to treat ED and disordered eating by helping individuals identify and challenge negative thought patterns related to food and body image. Therapy helps individuals explore the emotional triggers for disordered eating behaviors and develop healthier coping mechanisms.
Nutrition therapy helps individuals rebuild a healthy relationship with food by addressing any nutrient deficiencies, re-establishing balanced eating habits, and reducing anxiety around food. A nutritionist can guide individuals through creating a meal plan that meets their needs and helps them understand the role food plays in supporting both physical and mental health.
Mindfulness helps individuals become more aware of their thoughts, feelings, and physical sensations without judgment. In the context of ED and disordered eating, mindfulness practices, like mindful eating and meditation, can help break the cycle of obsessive thoughts about food and encourage a more balanced, compassionate approach to eating.
Functional medicine supports recovery from ED and disordered eating by addressing underlying physiological factors such as hormonal imbalances, nutrient deficiencies, and gut health issues. By optimizing physical health, functional medicine provides a foundation for emotional and psychological recovery. It focuses on restoring balance in the body to help individuals regain trust in their bodies and reduce unhealthy eating patterns.
Yes, recovery from ED and disordered eating is possible with the right treatment and support. The recovery process may take time, but with a combination of therapy, nutritional counseling, mindfulness, and support, individuals can develop healthier eating behaviors, improve self-esteem, and regain control over their relationship with food. Modyfi’s integrative approach provides comprehensive care to support long-term recovery and healing.










